rheumatoid arthritis
Expert Physiotherapy at Home
Personalised Recovery Programmes
Trusted Physiotherapists. Real Results.
Patient Testimonials
Our Medical Team
Meet some of our experienced and dedicated healthcare professionals
Dr. Lokesh G
15 Years Experience
SPECIALIZATIONS
Experienced in Neurological rehabilitation, Orthopaedic physiotherapy, and Paediatric care
Delivers structured, high-impact treatment plans across neuro, ortho, and paediatrics—ensuring safety, comfort, and measurable recovery at every stage.
Dr. Mohammed Sarwar
15 Years Experience
SPECIALIZATIONS
Experienced in Neurological rehabilitation, Adult physiotherapy, and Paediatric care
Combines deep clinical expertise with a compassionate approach, supporting both adults and children through neuro and physical rehabilitation that promotes long-term independence and recovery.
Dr. Nelapati Divya
12 Years Experience
SPECIALIZATIONS
Skilled in Orthopaedic rehabilitation, Manual therapy techniques, and Paediatric physiotherapy
Brings a personalised, hands-on approach to healing—combining structural expertise with paediatric sensitivity to restore movement, relieve pain, and improve everyday function.
Dr. Naveen V
3 Years Experience
SPECIALIZATIONS
Trained in Pain management, Cardiac and Orthopaedic rehabilitation, Neurological care, and Neural tissue mobilisation
Brings clinical precision and empathy together—designing science-backed recovery protocols for pain relief, nerve mobilisation, and cardio-neuro-ortho rehabilitation across all age groups
Dr. Miloni Savla
2 Years Experience
SPECIALIZATIONS
Holds an MPT in Orthopaedics with a focus on Musculoskeletal rehabilitation and strength recovery
Delivers focused, movement-oriented therapy grounded in orthopaedic science—helping patients rebuild strength, restore function, and return to daily life with confidence

what is rheumatoid arthritis?
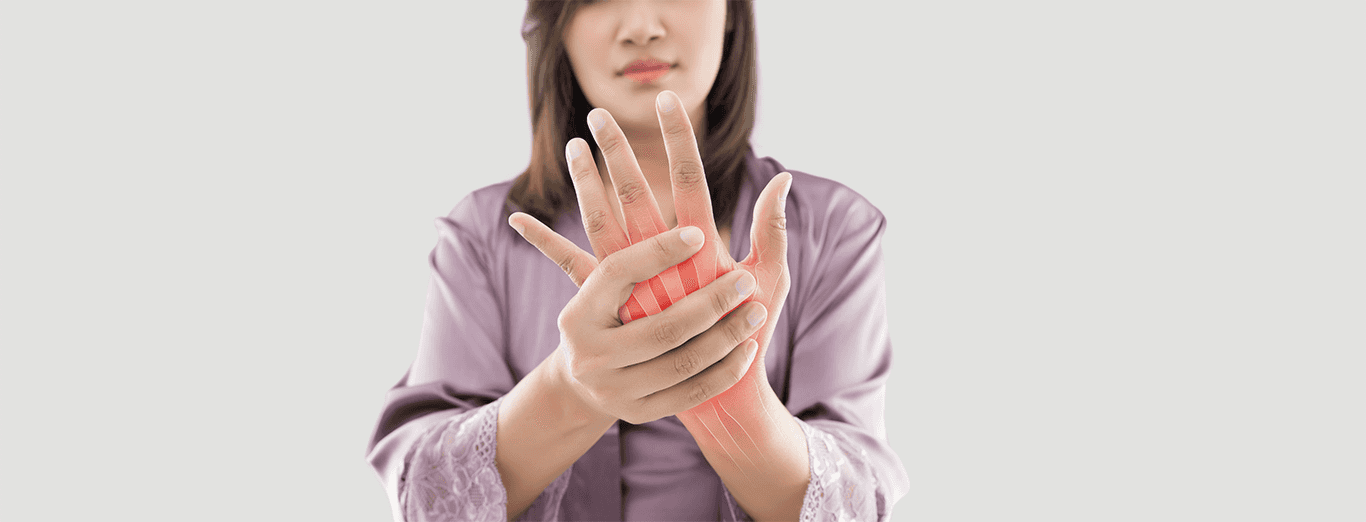
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that affects the body. In this disease, the immune system, tasked with protecting the body from bacteria and viruses, starts attacking its own body tissues and the joints of the body, causing inflammation of the joints which results in painful deformity and immobility of the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis primarily affects the fingers, wrists, feet and ankles.
rheumatoid arthritis symptoms:
Rheumatoid arthritis symptoms vary in severity among different people and the symptoms also have the nature of completely vanishing and returning intermittently. The varied symptoms associated with rheumatoid arthritis are;
- Fatigue: Persistent and overwhelming tiredness or exhaustion.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature often accompanies flare-ups.
- Joint pain: Discomfort or pain in the joints, a hallmark of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Joint tenderness and inflammation: Sensitivity and swelling in affected joints due to inflammation
- Restricted mobility and stiffness: Difficulty moving joints, stiffness, especially in the morning or after inactivity.
- warmth and redness of the joint: Increased temperature and redness around affected joints.
- Anemia: Decreased red blood cell count, leading to fatigue and weakness.
- Loss of joint function and limping: Gradual reduction in joint functionality, potentially causing a limp.
- Many joints are affected simultaneously and can occur on both sides of the body.
These Might be of Interest
pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis:
Rheumatoid Arthritis essentially originates as a condition of continuous cell activation leading to autoimmunity and immune complex in the joints and organs. The initial site of the ailment is the synovial membrane, where swelling and blockages prompt invasion of immune cells.
- Non specific inflammation: The varied genetic disorders leading to the onset of the unusual immune response becomes permanent and chronic once initiated. People affected with rheumatoid arthritis have abnormal glycosylated antibodies that are chiefly responsible for joint inflammation.
- Synovium Amplification: With the onset of the unusual autoimmune response, it may take a few years for it to completely establish itself; after which the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis begin to manifest. The plasma cells derived from B lymphocytes produce rheumatoid factors in large quantities, which through various related processes finally result in inflammation of the joints.
- Persistent Inflammation: This is the stage when the disease progresses and forms granulation tissues on the edges of the synovial lining, pannus with extensive angiogenesis and enzymes resulting in tissue damage. The synovium then thickens and the cartilage and the underlying bones and joints start to disintegrate.
rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis:
It is difficult to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis in its early stages as its early symptoms are similar to other ailments. The first step in rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis is physical examination by a Rheumatologist to check the severity of the swelling, redness, warmth, reflexes and muscle strength. Besides that the other diagnostic tools that can be used to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis are blood tests, MRI scan, ultrasound and X – rays.
rheumatoid arthritis causes:
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks its own body tissues and joints. Researchers are still clueless as to why the immune system begins to behave in this unusual manner. However, a few contributing rheumatoid factors have been identified as rheumatoid arthritis causes. These rheumatoid factors are as follows;
Genetic factors: Genetic plays an indirect and minor factor in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. The gene – HLA has been found as a common rheumatoid factor in a few patients of rheumatoid arthritis. However, all those affected with rheumatoid arthritis do not necessarily have the HLA gene present in their body, meaning the HLA gene makes a person susceptible to the diseases but is not the direct cause of RA.
Environment Factors: Few environmental factors in interaction with genetic factors put a person at a greater risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. These environmental factors;
- Bacteria and viruses
- Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke
- Air pollution
- Exposure to certain chemicals and insecticide
Personal Factors: Personal factors like age, gender and hereditary also play a role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis.
Age: rheumatoid arthritis mainly affects people in the age group of 40 to 60 years but it is not a necessity and can affect people across any age group.
Gender: Although both men and women are affected with rheumatoid arthritis but, women are more prone to rheumatoid arthritis than men.
Hereditary: People having rheumatoid arthritis in their family history are more susceptible to rheumatoid arthritis than others.
home remedies for rheumatoid arthritis
Here are a few home remedies for rheumatoid arthritis;
- Regular practice of rheumatoid arthritis exercises as suggested by a physiotherapist
- Applying hot and cold compress
- Taking fish oil supplements
- Drinking turmeric infused water or milk
- Apple cider vinegar mixed with honey and warm water proves effective in rheumatic pain
- Taking Garlic capsules or eating raw garlic daily also help relief rheumatic pain
- Soaking in warm water mixed with Epsom salt helps in rheumatism.
- Massaging ginger oil can also help with rheumatism.
- Following proper rheumatoid arthritis diet as recommended by a dietician
rheumatoid arthritis treatment:
As of now there is no found rheumatoid arthritis cure in rheumatoid arthritis treatment plan. Till date, the main aim of rheumatologist’s is to help in reducing the joint inflammation and pain, increasing function, prevention of further joint deterioration and deformity and reduce rheumatic pain. The usual course of action in rheumatoid arthritis treatment is medication, therapy and surgery.
- Medication: The basic medication offered for rheumatism treatment is non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs, analgesics, corticosteroid medications, disease modifying anti -rheumatic drugs and biologic agents.
- Physical therapy for rheumatoid arthritis – Rheumatologists often recommends the patients to seek Physical therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Physical therapy for rheumatoid arthritis offers specifically designed rheumatoid arthritis exercises to help in the mobility and the flexibility of the joints and to reduce rheumatic pain.
- Surgery: Surgery is often used in rheumatism treatment as a last form of rheumatoid arthritis cure to help the patient in regaining some joint movement back. The various surgical procedures that a rheumatologist can recommend are, Synovectomy, Tendon repair, Joint Fusion, Joint Replacement
how can we help?
Portea recognizes the unique challenges faced by individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, particularly in terms of mobility and overall well-being. We are dedicated to offering physical therapy in rheumatoid arthritis at your home, specifically designed for those with rheumatoid arthritis.
Our expert healthcare team provides comprehensive physiotherapy for rheumatoid arthritis, encompassing medication administration and personalized therapy plans. Our approach is holistic, focusing not only on treatment but also on patient education about effective exercises for rheumatoid arthritis, which are crucial in reducing pain, enhancing mobility, and increasing flexibility. You can find by searching for physiotherapy for rheumatoid arthritis near me.
Opting for Portea means receiving continuous, high-quality care that significantly improves the quality of life for rheumatoid arthritis patients. We are committed to not just delivering routine healthcare but also positively impacting our clients’ overall well-being, helping them achieve greater mobility and a more enjoyable life.
With Portea, you’re not just getting a service ; you’re gaining a partner in your journey to recovery and well-being. We also offer a range of superior healthcare services, including doctor consultations, medical equipment, nursing home care, and dedicated caretakers. Rely on us for top-tier healthcare solutions tailored to your requirements.
references
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rheumatoid-arthritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20353648
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rheumatoid_arthritis
- https://www.arthritis.org/about-arthritis/types/rheumatoid-arthritis/what-is-rheumatoid-arthritis.php
- https://www.webmd.com/rheumatoid-arthritis/default.htm
faqs
How can one effectively manage rheumatoid arthritis?
Incorporate exercises and relaxation techniques into your routine to alleviate pain and maintain an active lifestyle. Foster open communication with your healthcare team to gain greater control over your condition. Seek support to cope with the physical, emotional, and mental challenges associated with rheumatoid arthritis.
What are the sensations associated with rheumatoid arthritis?
Inflammation, warmth, and redness characterize the affected joints. The inflammation of the joint lining can lead to swelling, causing the joints to become hot and tender to the touch. Additionally, some individuals may develop firm swellings known as rheumatoid nodules beneath the skin around the affected joints.
Which foods are recommended for arthritis?
- Broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, and cabbage – rich in sulforaphane.
- Fatty fish.
- Garlic.
- Tart cherries.
- Turmeric.
- Foods high in Vitamin C.
Who is susceptible to rheumatoid arthritis?
A higher prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis is observed in women compared to men, with approximately two to three times more women affected by the disease. Researchers believe that reproductive and hormonal factors might contribute to the development of the condition in some women. Additionally, family history and genetic factors play a role in susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis.
What measures can be taken to reduce the risk of rheumatoid arthritis?
- Quit smoking.
- Adopt a Mediterranean diet rich in vegetables, fruits, olive oil, nuts, and whole grains.
- Engage in 20-30 minutes of daily exercise.
- Limit salt intake in your diet.
- Incorporate more fish and omega-3 fatty acids into your meals.
- Reduce consumption of sugar-sweetened soft drinks.
References
Doctor Consultation
Nursing
Physiotherapy
Trained Attendant
Elder Care
Mother & Baby Care
Lab Tests
Medical Equipment
Speciality Pharma
Critical Care