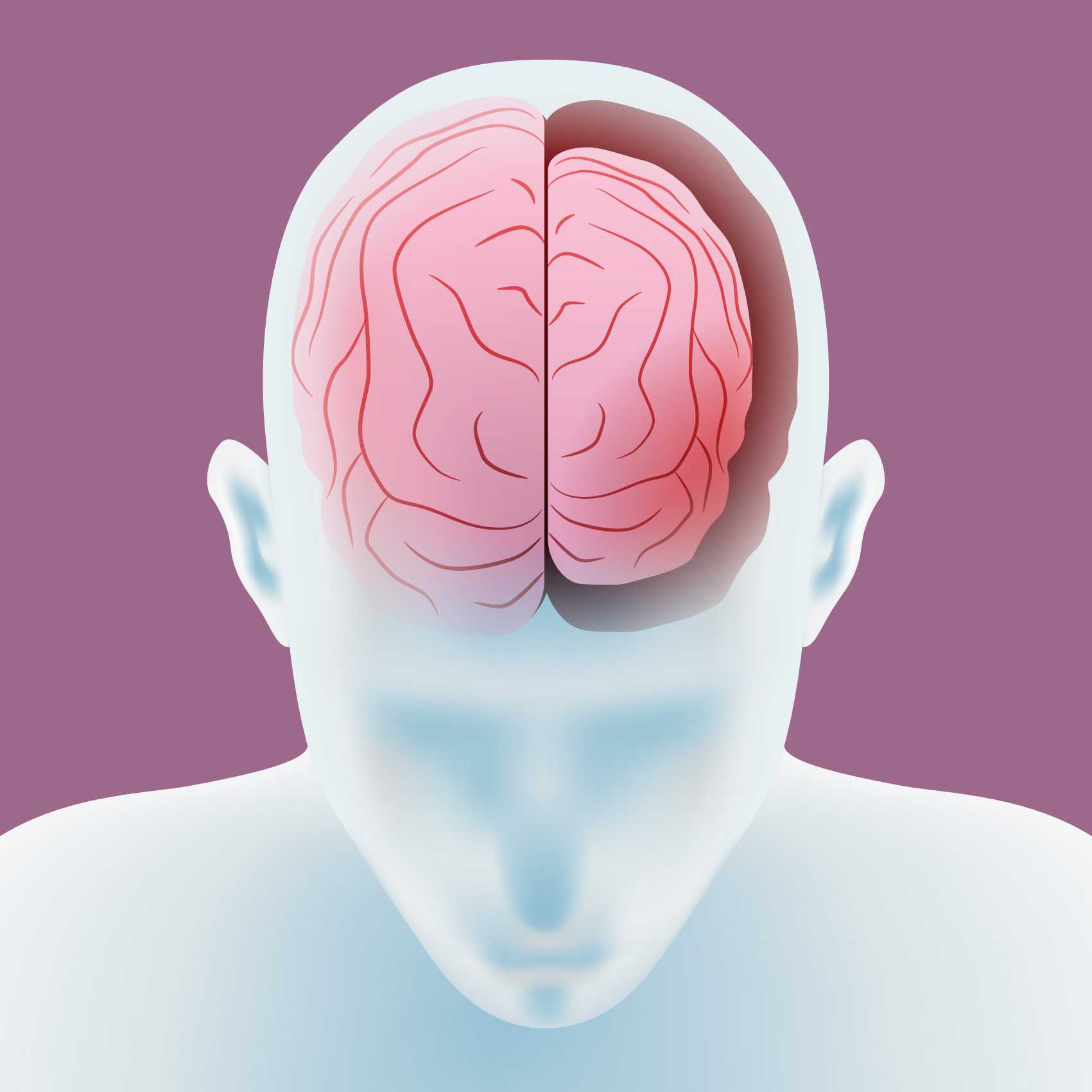
cerebral atrophy
Expert Physiotherapy at Home
Personalised Recovery Programmes
Trusted Physiotherapists. Real Results.
Patient Testimonials
Our Medical Team
Meet some of our experienced and dedicated healthcare professionals
Dr. Lokesh G
15 Years Experience
SPECIALIZATIONS
Experienced in Neurological rehabilitation, Orthopaedic physiotherapy, and Paediatric care
Delivers structured, high-impact treatment plans across neuro, ortho, and paediatrics—ensuring safety, comfort, and measurable recovery at every stage.
Dr. Mohammed Sarwar
15 Years Experience
SPECIALIZATIONS
Experienced in Neurological rehabilitation, Adult physiotherapy, and Paediatric care
Combines deep clinical expertise with a compassionate approach, supporting both adults and children through neuro and physical rehabilitation that promotes long-term independence and recovery.
Dr. Nelapati Divya
12 Years Experience
SPECIALIZATIONS
Skilled in Orthopaedic rehabilitation, Manual therapy techniques, and Paediatric physiotherapy
Brings a personalised, hands-on approach to healing—combining structural expertise with paediatric sensitivity to restore movement, relieve pain, and improve everyday function.
Dr. Naveen V
3 Years Experience
SPECIALIZATIONS
Trained in Pain management, Cardiac and Orthopaedic rehabilitation, Neurological care, and Neural tissue mobilisation
Brings clinical precision and empathy together—designing science-backed recovery protocols for pain relief, nerve mobilisation, and cardio-neuro-ortho rehabilitation across all age groups
Dr. Miloni Savla
2 Years Experience
SPECIALIZATIONS
Holds an MPT in Orthopaedics with a focus on Musculoskeletal rehabilitation and strength recovery
Delivers focused, movement-oriented therapy grounded in orthopaedic science—helping patients rebuild strength, restore function, and return to daily life with confidence

what is cerebral atrophy?
Cerebral atrophy refers to the progressive loss of neurons and the connections between them, leading to a reduction in brain size. This condition affects the brain’s structure and function, resulting in significant physical and cognitive challenges. While cerebral atrophy is often associated with aging, it can also occur due to specific medical conditions or lifestyle factors.
causes and contributing factors
One of the most common causes of cerebral atrophy is neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, or Huntington’s disease. Other contributing factors include traumatic brain injuries, stroke, prolonged alcohol abuse, infections like encephalitis, or autoimmune conditions like multiple sclerosis. Regardless of the cause, the loss of brain tissue can profoundly impact an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks.
symptoms and diagnosis
Symptoms of cerebral atrophy vary depending on the brain regions affected. Individuals may experience memory loss, reduced cognitive abilities, and impaired judgment. Physical symptoms such as difficulty in coordination, muscle weakness, and speech impairments are also common. These symptoms often worsen over time, emphasizing the need for early intervention and management.
risks associated with cerebral atrophy
Cerebral atrophy, characterized by the progressive loss of brain cells and connections, poses significant risks to cognitive and physical functioning. Individuals with this condition may experience memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and impaired motor skills, which can affect daily activities and independence. In severe cases, it can lead to dementia, seizures, or language difficulties. The atrophy also increases the likelihood of secondary complications, such as falls, injuries, and psychological challenges like depression or anxiety. Timely intervention and management are crucial to minimizing these risks and maintaining the best possible quality of life.
managing cerebral atrophy
While cerebral atrophy cannot be reversed, treatment focuses on slowing its progression and improving quality of life. This is achieved through a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, cognitive exercises, and rehabilitation therapies.
preventing cerebral atrophy
While some causes of cerebral atrophy, such as genetic disorders, cannot be prevented, adopting a brain-healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk or slow progression. Regular physical activity, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, and mental stimulation through learning and problem-solving activities can support brain health. Managing underlying conditions like hypertension, diabetes, or chronic infections is vital, as these can contribute to cerebral atrophy. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and exposure to neurotoxic substances further helps in prevention. Routine medical check-ups ensure early detection and management of risk factors.
the role of physiotherapy
Physiotherapy plays a pivotal role in addressing the physical challenges posed by cerebral atrophy. By engaging patients in exercises that improve muscle strength, flexibility, and coordination, physiotherapy helps maintain mobility and prevent complications like joint stiffness or falls.
portea’s cerebral atrophy physiotherapy services
At Portea, our Cerebral Atrophy services are designed to support individuals with cerebral atrophy in achieving their highest potential.
We also specialize in providing expert physiotherapy services for post-surgical rehab, arthritis, neuro-rehab, sports injury, orthopaedic physiotherapy, physiotherapy for elderly and more – all delivered conveniently at your home. Our dedicated team ensures you receive the personalized care you need for a smooth and successful recovery.
Portea provides a range of services to support your health, including nursing care at home, nursing attendants at home, and options to rent or purchase medical equipment at home. We also offer home vaccinations, personalized diabetes care plans, mothers and baby care plans at home. Our goal is to deliver compassionate, tailored care right where you need it.
portea’s physiotherapy services based on medical conditions
faq’s
What are the common symptoms of Cerebral Atrophy?
Symptoms vary widely but can include memory loss, confusion, difficulty with speech or language, behavioral changes, diminished coordination, and challenges in performing daily tasks.
How is Cerebral Atrophy diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves neurological examinations, cognitive evaluations, and imaging studies such as MRI scans or CT scans that help in visualizing structural changes in the brain.
Can Cerebral Atrophy be prevented?
While it is ordinarily not a preventable condition, the right lifestyle habits—balanced nutritional intake, exercise, mental stimulation, appropriate sleeping patterns, and managing risk factors like hypertension—may slow the progression of Cerebral Atrophy and lower the risk.
Is Cerebral Atrophy treatable or reversible?
A known cure that would lead to a total reversal of cerebral atrophy has not yet been identified. Treatment tends to be reserved for the symptomatic approach of this disorder; treatment usually aims at alleviating the symptoms, slowing down the progress, and improving the quality of life, such as medications, therapies, and support.
How would Cerebral Atrophy affect daily living issues?
It can impair one’s ability to think, remember, and communicate with one another. Patients may need someone to assist them with daily activities, for which they may need assistive devices and other kinds of therapy and caregiver support.
What kinds of therapy are generally beneficial to Cerebral Atrophy patients?
Physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and cognitive rehabilitation programs can help in enhancing mobility, communication, and cognitive function, thereby improving quality of life.
Doctor Consultation
Nursing
Physiotherapy
Trained Attendant
Elder Care
Mother & Baby Care
Lab Tests
Medical Equipment
Speciality Pharma
Critical Care











